With the remarkable increase in the number of mobile IoT devices, there is a growing demand for reliable and environmentally friendly power solutions to ensure their sustainable operation. As a result, the development of novel energy harvesting techniques has become increasingly urgent. Among them, flow-induced vibration energy harvesting, as a renewable and clean energy technology, is not only considered to play a crucial role in the decarbonization process of future energy systems but also has the potential to meet the energy needs of the increasingly popular mobile IoT devices for continuous and reliable operation.
Recently, Professor Wan Sun from Jiangsu University and his colleagues published a review article titled "Navigating the future of flow-induced vibration-based piezoelectric energy harvesting" in the top-tier energy journal Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews (IF=15.9). The paper explores the development of piezoelectric technology and materials, providing a comprehensive overview of the mechanisms, modeling techniques, and current development status of flow-induced vibration energy harvesters. Furthermore, it discusses various methods to improve the efficiency of piezoelectric energy harvesters, including optimizing structural configurations, adding nonlinear forces, applying multi-stable states, changing degrees of freedom, and optimizing interface circuits.Additionally, the article outlines several forward-looking areas for future research, including the utilization of metamaterials, integration of deep learning, and potential directions for commercialization, such as the construction of bladeless wind farms and the design of robust and environmentally stable energy harvesters. This study offers valuable insights and guidance for the advancement of flow-induced vibration energy harvesting technology.

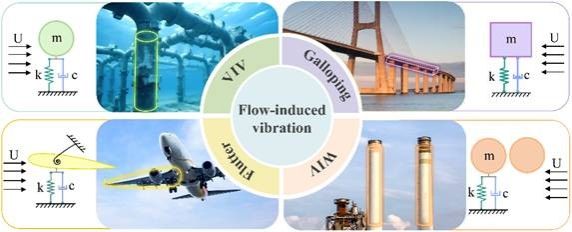
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of typical flow-induced vibration occurrence scenarios.
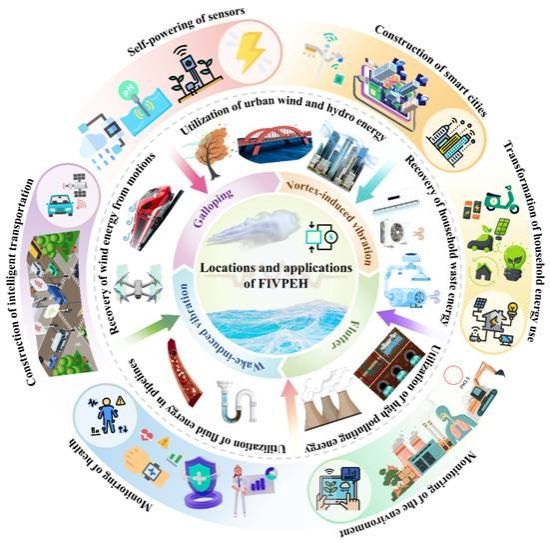
Figure 2. Potential locations and application scenarios of flow-induced vibration energy harvesters
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52105101, U23A20661, 92248301), the Jiangsu Provincial Special Fund for Technological Innovation (BE2022610), and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF2022R1A2C1007069). Professor Wan Sun from Jiangsu University and Professor Jongwon Seok from Chung-Ang University in Korea served as co-corresponding authors of the paper, with Professor Sun as the first author. Wang Yiheng, a graduate student, contributed as a co-author. Chung-Ang University and Southeast University were listed as collaborating institutions, and the School of Mechanical Engineering at Jiangsu University was credited as the primary affiliation for the paper.
Through the integration and discussion of the current research status and future developments in flow-induced vibration piezoelectric energy harvesting, this article is believed to guide more groundbreaking research in the right direction and provide a useful and rich reference for professionals in this field. It will help coordinate interdisciplinary research, establish broad collaborations, and further promote the practical application and commercialization of flow-induced vibration piezoelectric energy harvesting.
Article link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1364032124003502
